In the world of dairy farming, technological advancements are reshaping traditional practices, and smart milking systems stand out as a revolutionary tool.
With the demand for dairy products growing globally and the need for efficient, sustainable farming practices becoming more urgent, these systems are transforming how dairy farmers manage their operations.
From increasing milk yield to improving animal health, smart milking systems offer substantial benefits to farmers and the dairy industry at large.
The Evolution of Milking Technology
Historically, milking was a labor-intensive task done by hand, and later, with the help of rudimentary mechanical milking machines. These early technologies, while a step forward, required significant manual oversight, were prone to errors, and didn’t provide the real-time data farmers needed to make informed decisions.
As dairy farms scaled up, the demand for more efficient, automated, and data-driven systems became clear.
Today, smart milking systems integrate automation, sensors, data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) to create a seamless process that benefits both farmers and livestock. These systems allow farmers to monitor the milking process in real-time, ensuring efficiency, quality, and animal welfare.
Key Components of Smart Milking Systems
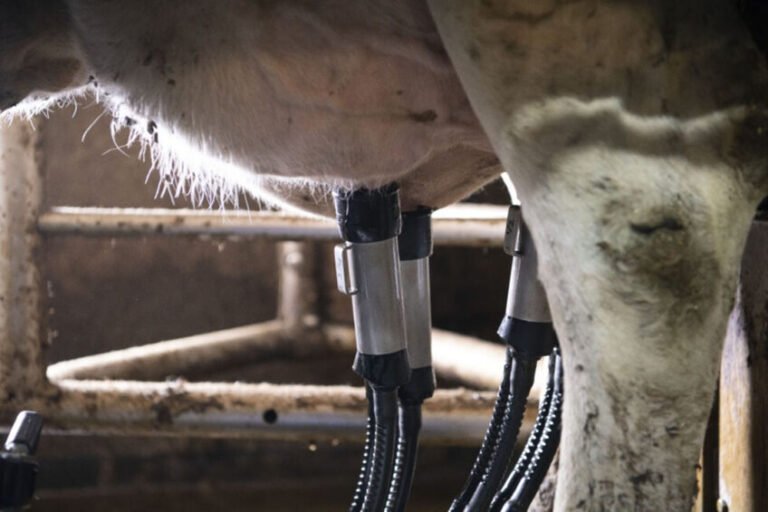
- Automated Milking Machines (AMMs): AMMs are the core of any smart milking system. These machines not only automate the physical act of milking but also collect real-time data on the cow’s milk output, health status, and behavior. AMMs can detect when a cow is ready to be milked and perform the process with precision, ensuring optimal milk extraction and reducing stress on the animal.
- Sensors and Monitoring Devices: Sensors play a critical role in smart milking systems. They monitor everything from milk quality (such as fat content and temperature) to cow health indicators like activity levels, rumination, and even body temperature. This data is fed into a central system where it can be analyzed for insights on both individual cows and herd-wide trends.
- Data Analytics and AI: Data collected from sensors and milking machines are processed using advanced analytics and AI algorithms. These tools help farmers make decisions about feeding, breeding, and veterinary care. For instance, AI can detect early signs of mastitis—a common and costly dairy cow infection—before it becomes a severe issue, allowing for timely intervention. Data-driven insights also optimize milk production by identifying peak production times and customizing feeding schedules for better yields.
- Cloud-based Management Platforms: Many smart milking systems are integrated with cloud-based platforms where farmers can access real-time data and performance reports from any device, anywhere. This remote access to data streamlines farm management, especially for larger operations with multiple facilities.
- Robotics and Automation: In addition to automated milking, some advanced systems use robotics to handle other dairy tasks like feeding, cleaning, and even cow herding. These robots work in tandem with the milking machines, creating a fully automated dairy operation.
Benefits of Smart Milking Systems
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Automation significantly reduces the time and labor involved in milking cows, allowing farmers to focus on other aspects of farm management. Automated systems can milk cows 24/7, increasing the frequency of milking and, as a result, boosting milk production. Studies have shown that farms using smart milking systems can experience up to a 10-15% increase in milk yields.
- Enhanced Milk Quality: By monitoring milk quality in real-time, smart milking systems ensure that only the best-quality milk is collected. Contaminated milk, whether due to illness in cows or environmental factors, can be quickly detected and isolated, ensuring a consistent product for processors and consumers.
- Improved Animal Health and Welfare: The data generated by smart milking systems provide farmers with a deeper understanding of each cow’s health. Early detection of illnesses, stress, or injury ensures that cows receive prompt treatment, reducing the risk of disease spreading within the herd. Automation also minimizes human handling, reducing stress on the animals during the milking process.
- Cost Savings: While the initial investment in smart milking systems can be significant, the long-term savings are considerable. Reduced labor costs, lower veterinary bills due to preventive health care, and increased milk production all contribute to a quick return on investment. Additionally, optimizing feed and care based on data insights reduces waste and enhances farm sustainability.
- Sustainability: Many smart systems are designed with sustainability in mind. By optimizing resource use, such as water and feed, and reducing energy consumption through automation, smart milking systems contribute to more eco-friendly farming practices. Furthermore, the ability to monitor cow emissions and overall farm environmental impact helps farmers comply with global sustainability standards.
Challenges and Considerations
While smart milking systems offer numerous benefits, they are not without challenges. The initial cost of investment can be high, which may be a barrier for small to mid-sized farms. Additionally, there is a learning curve associated with the adoption of these technologies. Farmers must be comfortable using software, analyzing data, and managing new equipment. Technical issues, such as system malfunctions or software glitches, can also disrupt operations.
To fully leverage the potential of smart milking systems, farmers need access to proper training and support. Many technology providers offer comprehensive onboarding and technical assistance to ease the transition and ensure systems are running smoothly.
The Future of Smart Milking Systems
As technology continues to advance, smart milking systems will become even more sophisticated. The integration of AI, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) will further enhance automation and data analytics capabilities. In the future, farmers may see entirely self-sustaining dairy farms where AI manages every aspect of production, from feeding to milking to distribution.
Additionally, as the demand for sustainable and humane farming practices grows, smart milking systems will be essential in helping dairy farms meet environmental regulations and consumer expectations. Precision farming tools that track the carbon footprint and optimize resources are likely to become standard, ensuring the future of dairy farming is both profitable and sustainable.
Conclusion
Smart milking systems are revolutionizing dairy operations, offering a blend of efficiency, productivity, and animal welfare that was previously unattainable.
As the technology evolves, these systems will play an even more vital role in shaping the future of dairy farming, helping farmers meet global demands while operating sustainably.
For modern dairy farmers, investing in smart milking technology is no longer just an option—it’s becoming a necessity to stay competitive and ensure long-term success in a rapidly changing industry.
Also Read